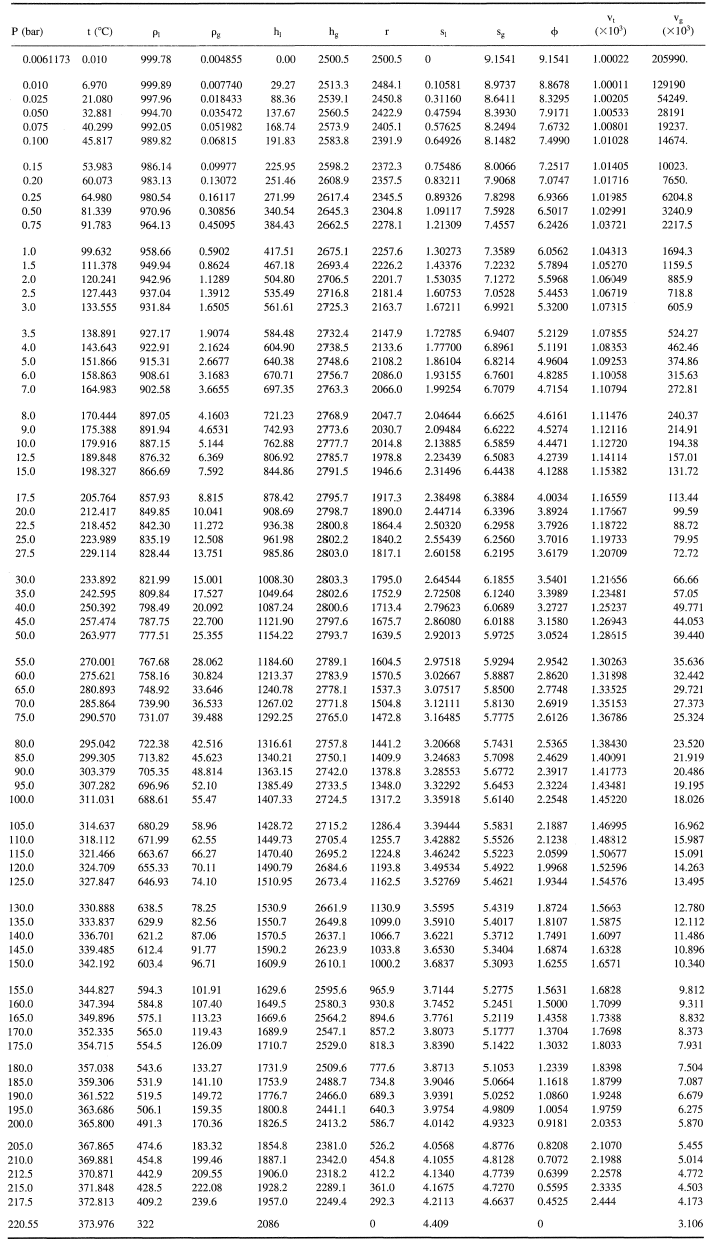
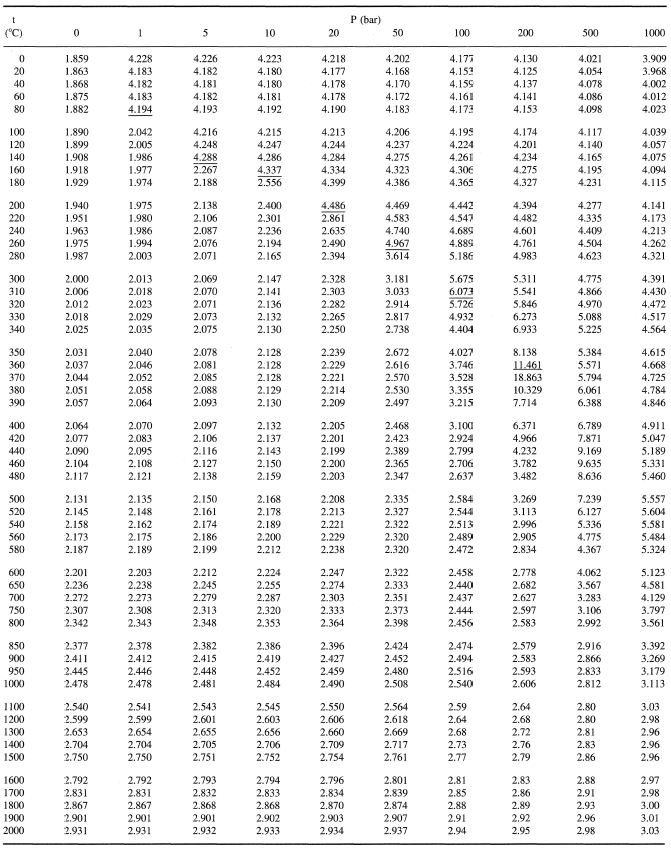
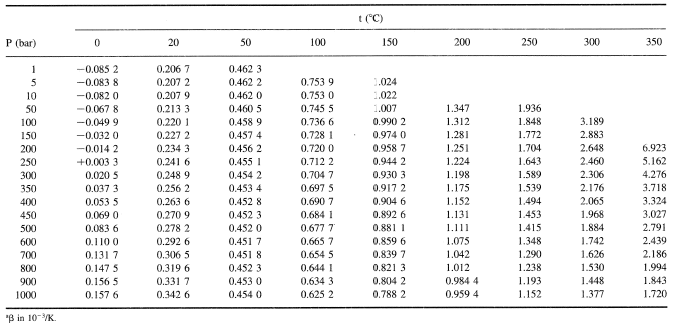
The following tables of the properties of steam are taken directly from Chapter 5.5.3 of the Heat Exchanger Design Handbook, 1986, by C. F. Beaton.
The tables in this section are reprinted, with permission, from NBS/NRC Steam Tables.
| Symbol | Property | Units |
| h | specific enthalpy | kJ/kg |
| P | pressure | bar = 0.1 MPa |
| Pr | Prandtl number (= ηCp/λ) | dimensionless |
| r | specific enthalpy of vaporization | kJ/kg |
| s | specific entropy | kJ/(kg K) |
| ts | temperature at saturation | |
| u | specific internal energy | kJ/kg |
| ν | specific volume | m3/kg |
| ε | static dielectric constant | dimensionless |
| η | viscosity | 10−6 kg/(s m) = MPa s |
| λ | thermal conductivity | mW/(K m) |
| ρ | density | kg/m3 |
| σ | surface tension | kg/s2 = N/m |
 |
specific entropy of vaporization | kJ/(kg K) |
| g | denotes a saturated vapor state |
| l | denotes a saturated liquid state |
The reference state for all property values is the liquid at the triple point, for which state the specific internal energy and the specific entropy have been set to zero.
Table 8. Properties for coexisting phases: viscosity, thermal, conductivity, Prandtl number, dielectric constant, surface tension

Table 9. Thermal expansion coefficient β = (1/ν)(∂ν/∂T)p of liquid water as a function of pressure and temperature. (β in 10−3/K.)
References
- Haar, L., Gallagher, J. S., and Kell, G. S. (1984) Thermodynamic and Transport Properties and Computer Programs for Vapor and Liquid States of Water in S.I. Units. NBS/NRC, Hemisphere, Washington, D.C.
- VDI-Wärmeatlas (1974) 2d edn., Verein Deutsches Ingenieure, Dusseldorf. DOI: 10.1002/cite.330470908